Nucleolar Knowledge Base (NKB) User Guide
Complete guide for navigating and utilizing the NKB platform
Table of Contents
- Knowledge Base Overview
- Quick Start
- Query Methods Guide
- Detailed Operation Guide
- Advanced Features
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Technical Specifications
- Contact Us
1. Knowledge Base Overview
1.1 What is NKB?
The Nucleolus Knowledge Base (NKB) is a comprehensive knowledge and potential insight repository focused on nucleolar biology and related diseases, built from literature databases including PubMed.
1.2 What information does NKB provide?
- Evidence-based knowledge and potential insights in the precise form of Triples, Subject-Predicate-Object (SPO), labelled with HIGH/MIDDLE/LOW CONFIDENCE
- Evidence-based mini-review based on all obtained Triples or the HIGH CONFIDENCE ones selected from confidence screening
- Knowledge graphs presented in a visualized tree structure display the hierarchical relationships and associations between knowledge entities
1.3 Core Data
1.4 Main Features
- Structured Knowledge Retrieval: Evidence-based conclusions in SPO triple format
- AI Review Generation: Automatically generate mini-reviews with citations based on literature
- Knowledge Graph Visualization: Hierarchical directory structure for knowledge discovery
- Three-Level Confidence Evaluation: HIGH/MIDDLE/LOW
2. Quick Start
➢ 3-Minute Quick Experience (for First-Time Users)
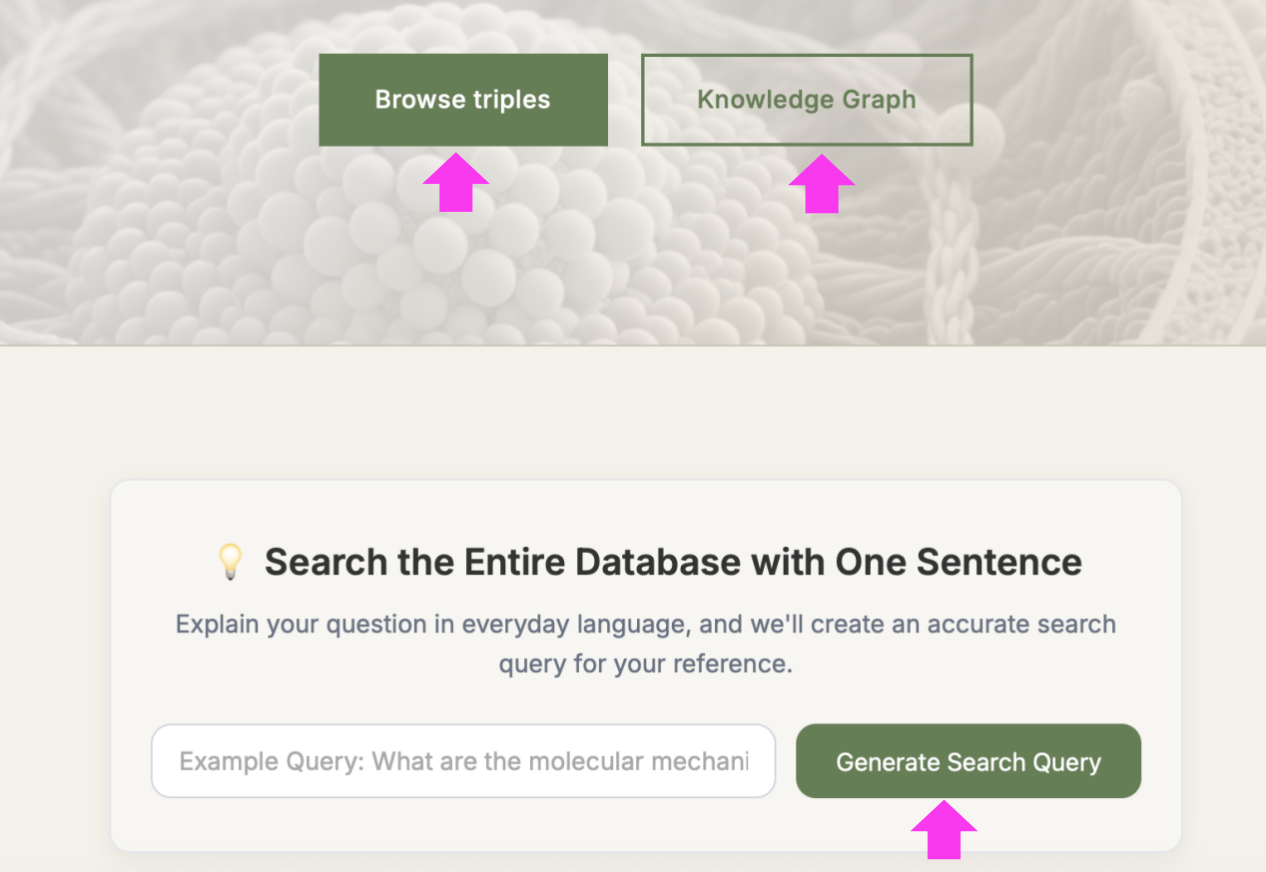
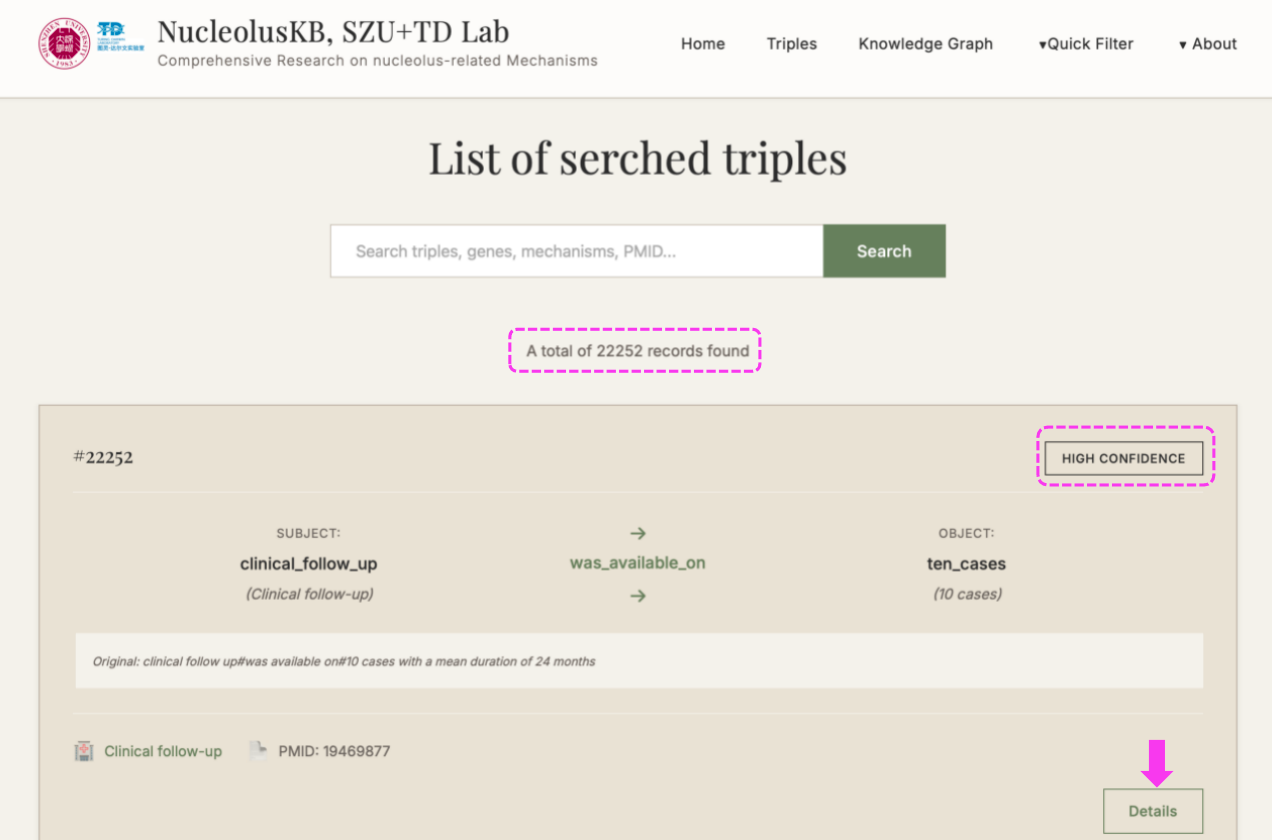
(1) Enter Homepage → Click → The following new page with 22252 Triples listed for the entire Knowledge Base.
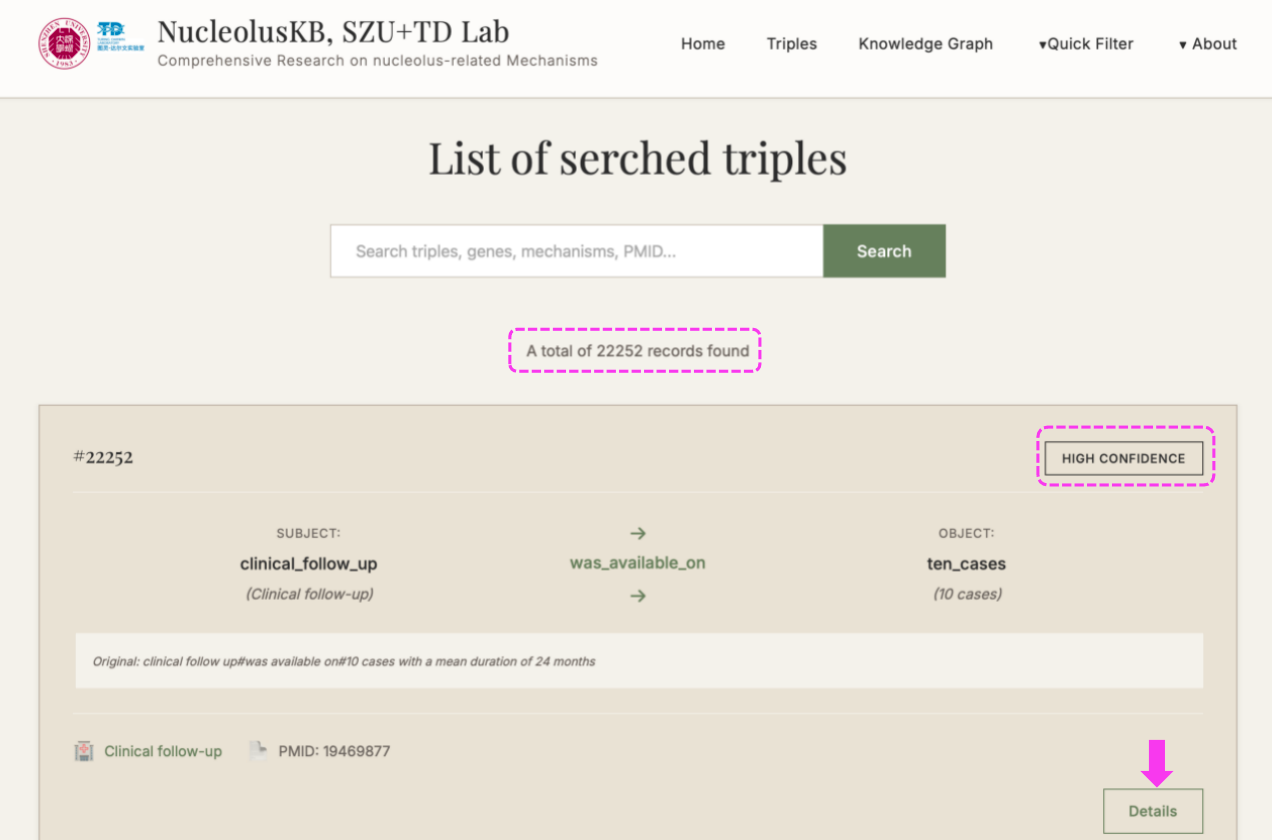
Each triple is equipped with a label of HIGH/MIDDLE/LOW CONFIDENCE on the right top, so that you can find the high confidence Triples that are based on solid facts.
On the right bottom, you can click the for more detailed information for this current Triple.
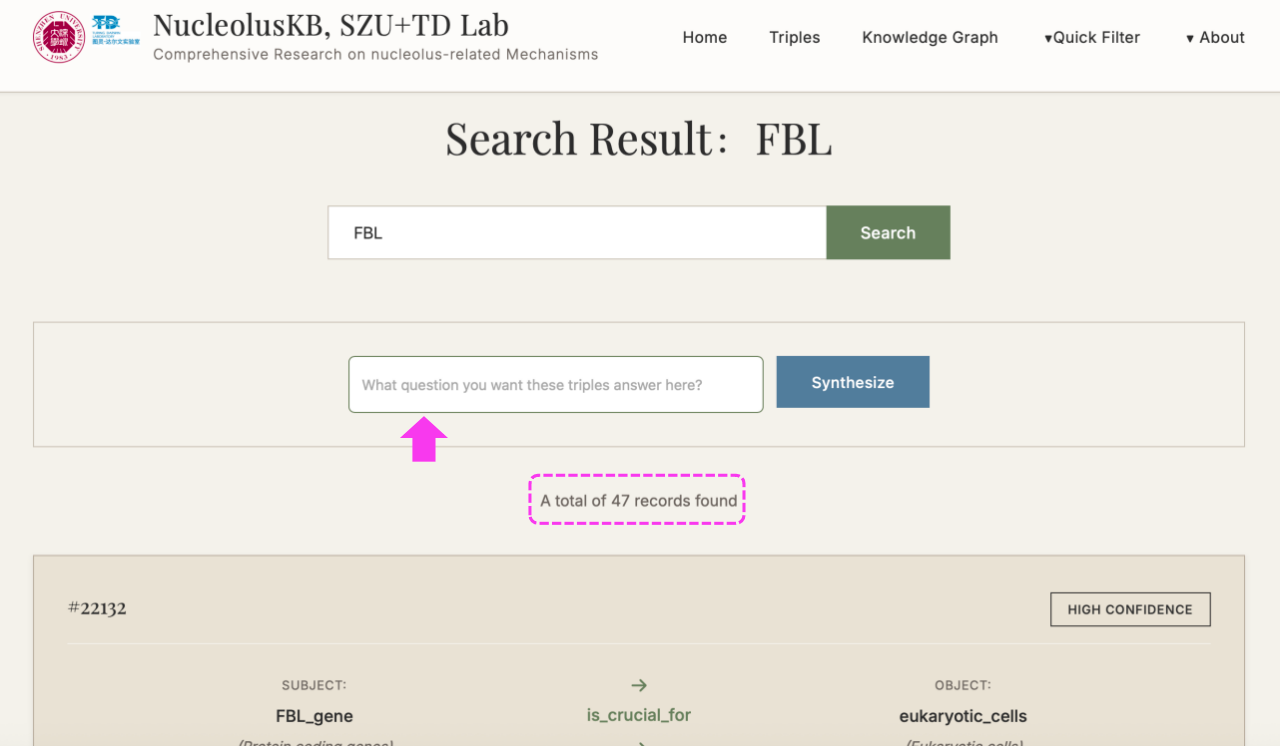
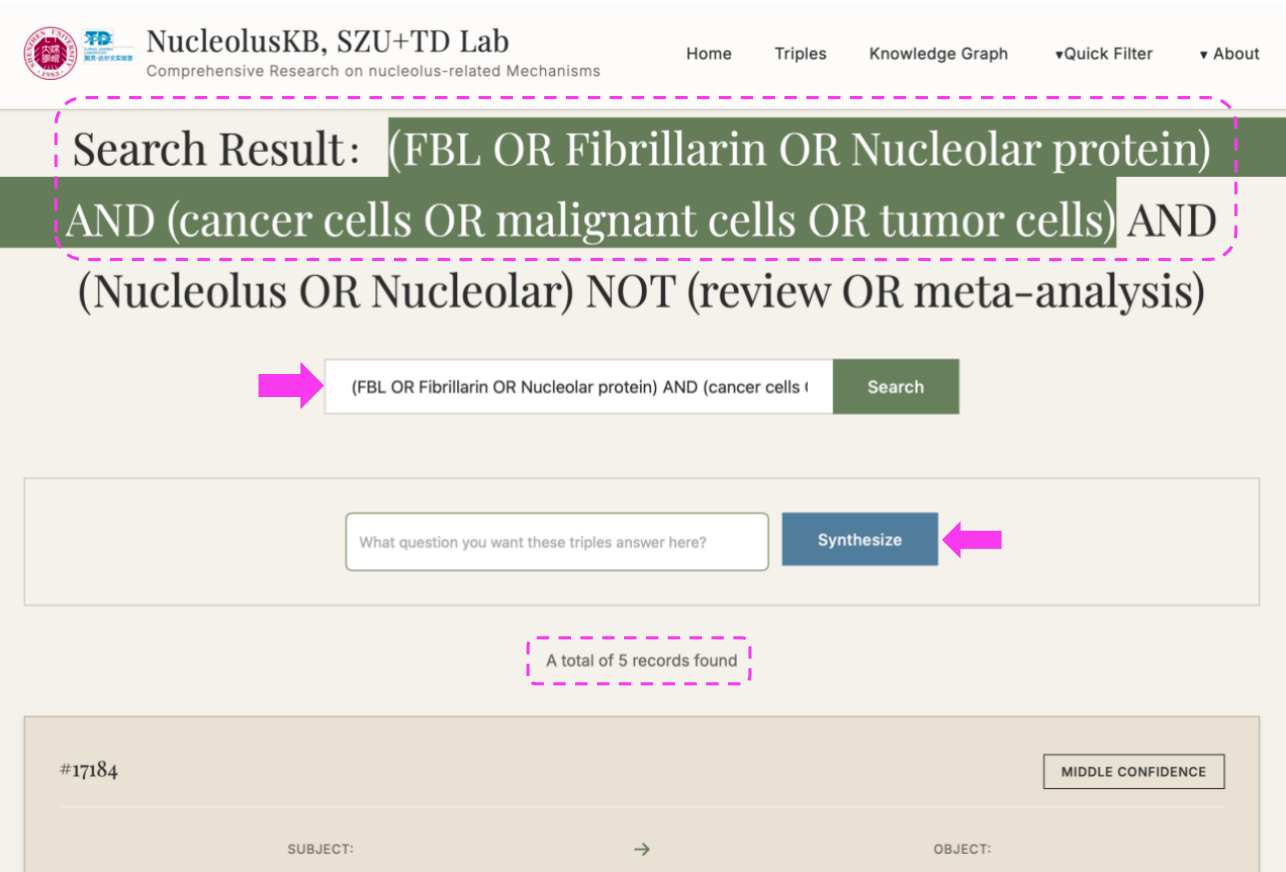
(2) Enter keywords (e.g. FBL) in the query box → Click
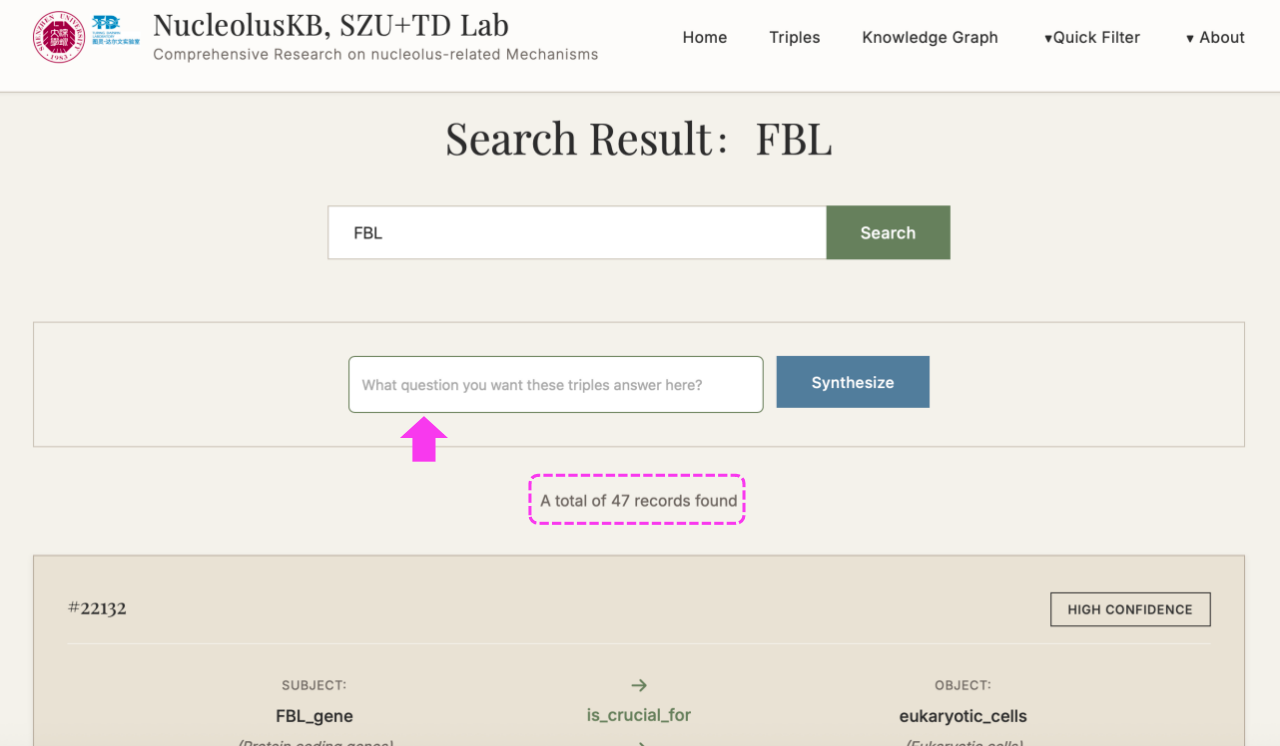
A subset of keyword-related Triples listed at the bottom.
New searching box appears with button on the right.
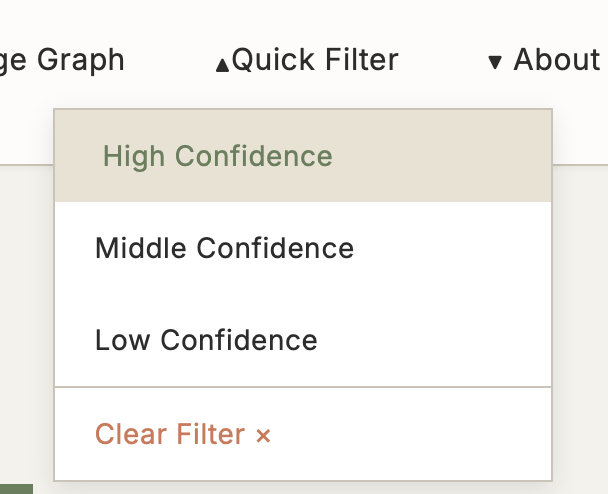
(3) Enter a question in the query box, e.g. "what is the function of FBL in cancer cells" → click → Select the desired confidence range (If want to view all confidence level entries, click ) → click → "Synthesize" turned into "Thinking" → Wait for minutes → Receive a 200-500 word literature review with PMID citations
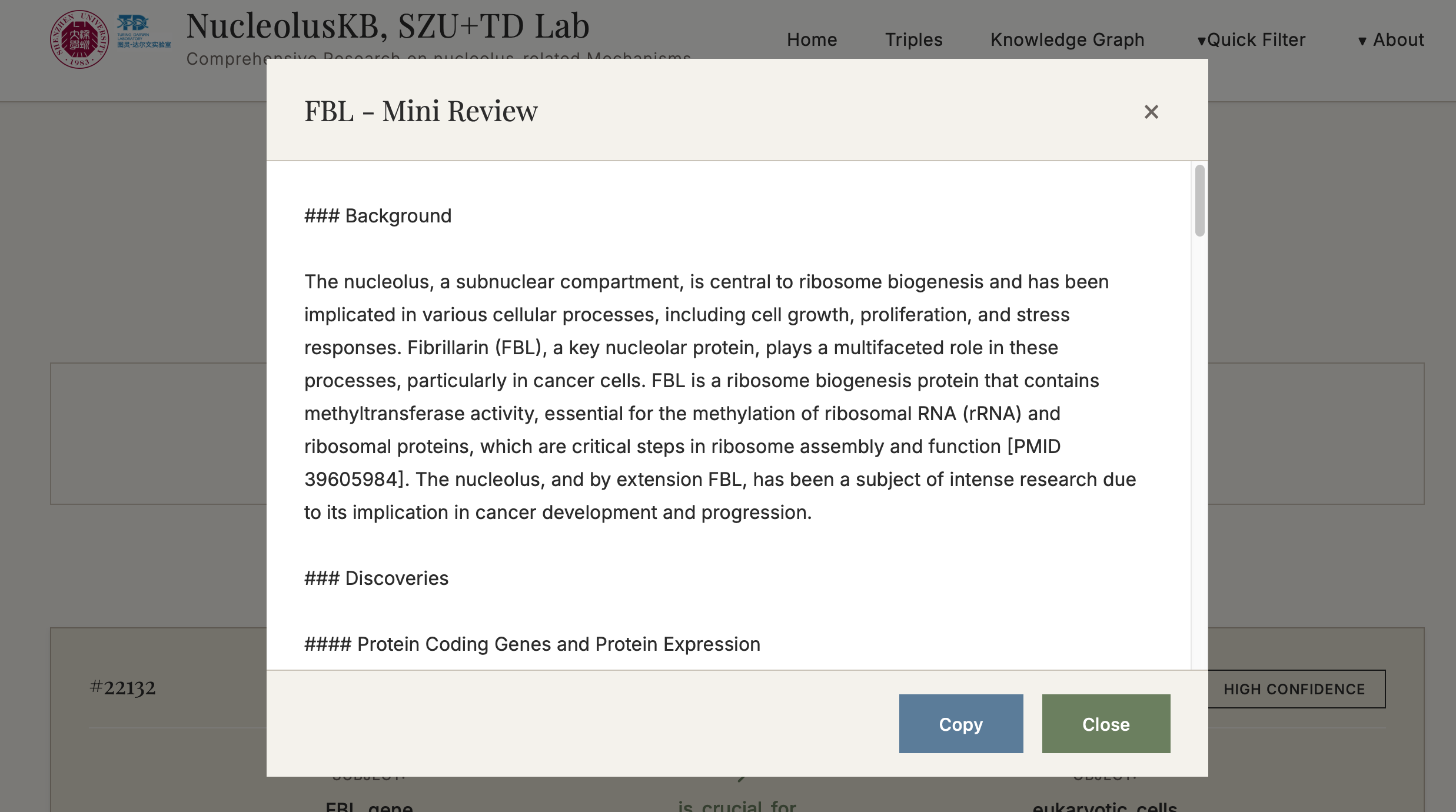
3. Query Methods Guide
3.1 Three query methods in the home page
| Query Method | Use Cases | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Browse Triples |
• Known specific gene/protein names • Need high-precision results |
Accurate conclusive descriptions with confidence filtering |
| Knowledge Graph |
• Exploratory research • Systematic learning |
Clear knowledge structure, easy discovery |
| Generate Search Query |
• Beginner-friendly • Complex question queries • Uncertain keywords |
Simple operation, intelligent recommendations |
3.2 How to Choose the Right Query Method?
🤔 My question is...
├─ "What is the role of NPM1 in cancer?"
│ └─ Recommended: Generate Search Query (Natural language)
│
├─ "I want to understand all knowledge related to nucleolar assembly"
│ └─ Recommended: Knowledge Graph (Systematic browsing)
│
└─ "Find specific functions of gene NPM1"
└─ Recommended: Browse Triples (Precise search)
3.3 Navigation Bar Functions
| Module | Function Description |
|---|---|
| Home | Homepage quick search entry |
| Triples | Browse and search SPO triples |
| Knowledge Graph | Categorized knowledge graph navigation |
| Quick Filter | Rapid filtering functionality |
| About | Platform information |
4. Detailed Operation Guide
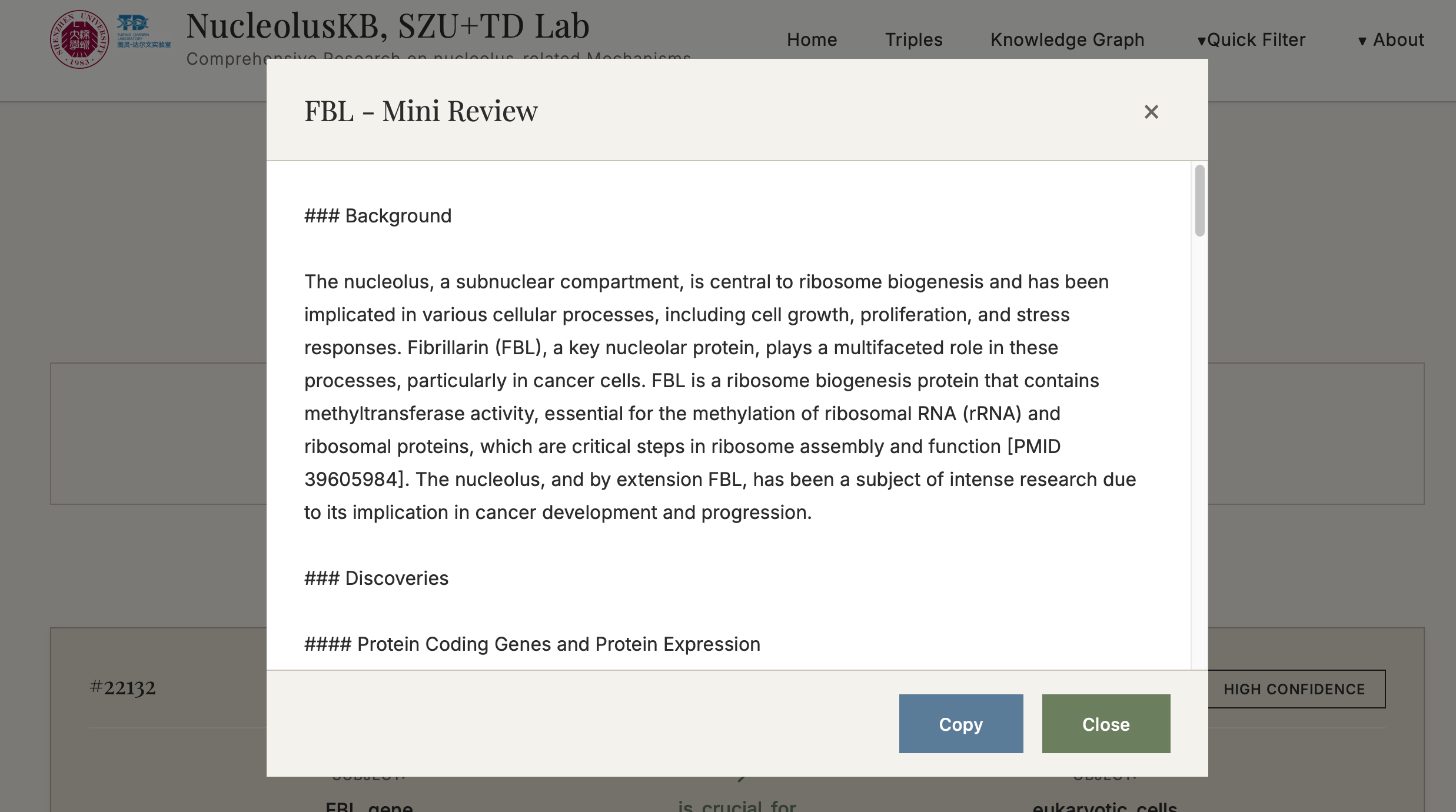
4.1 Browse Triples
Steps:
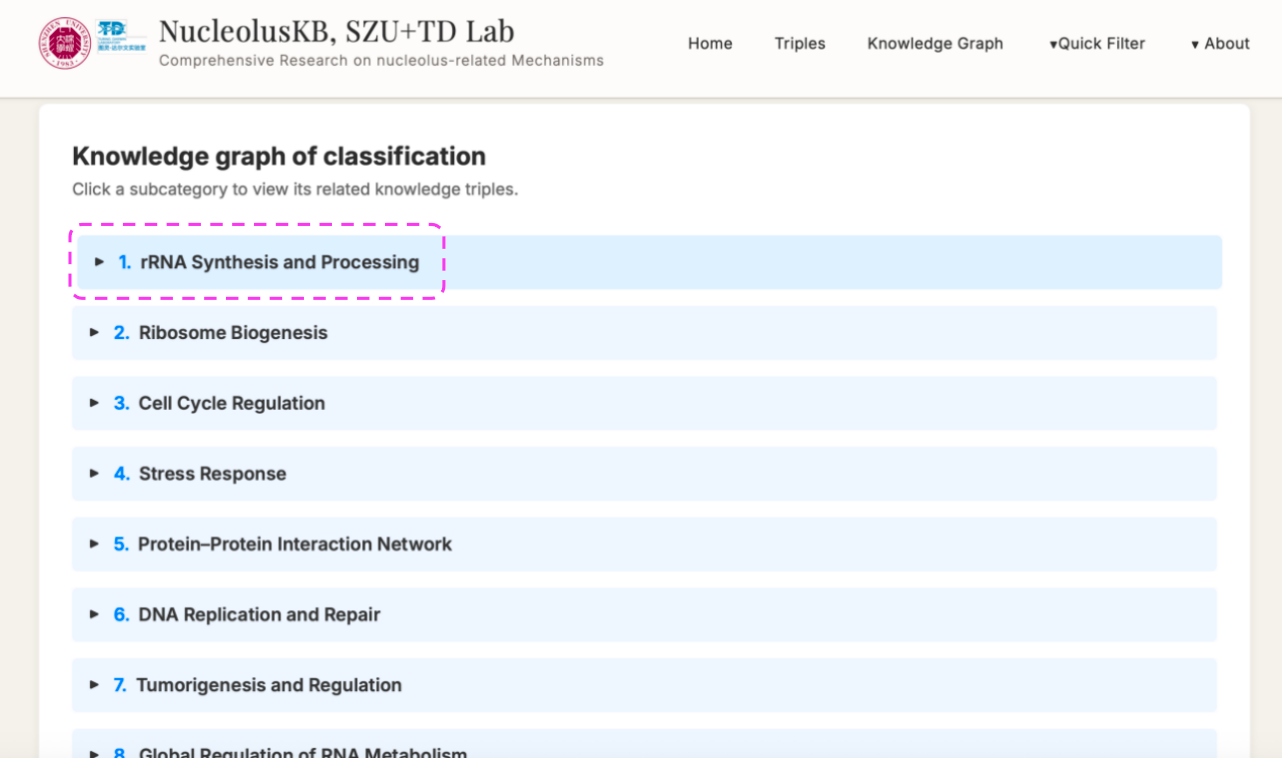
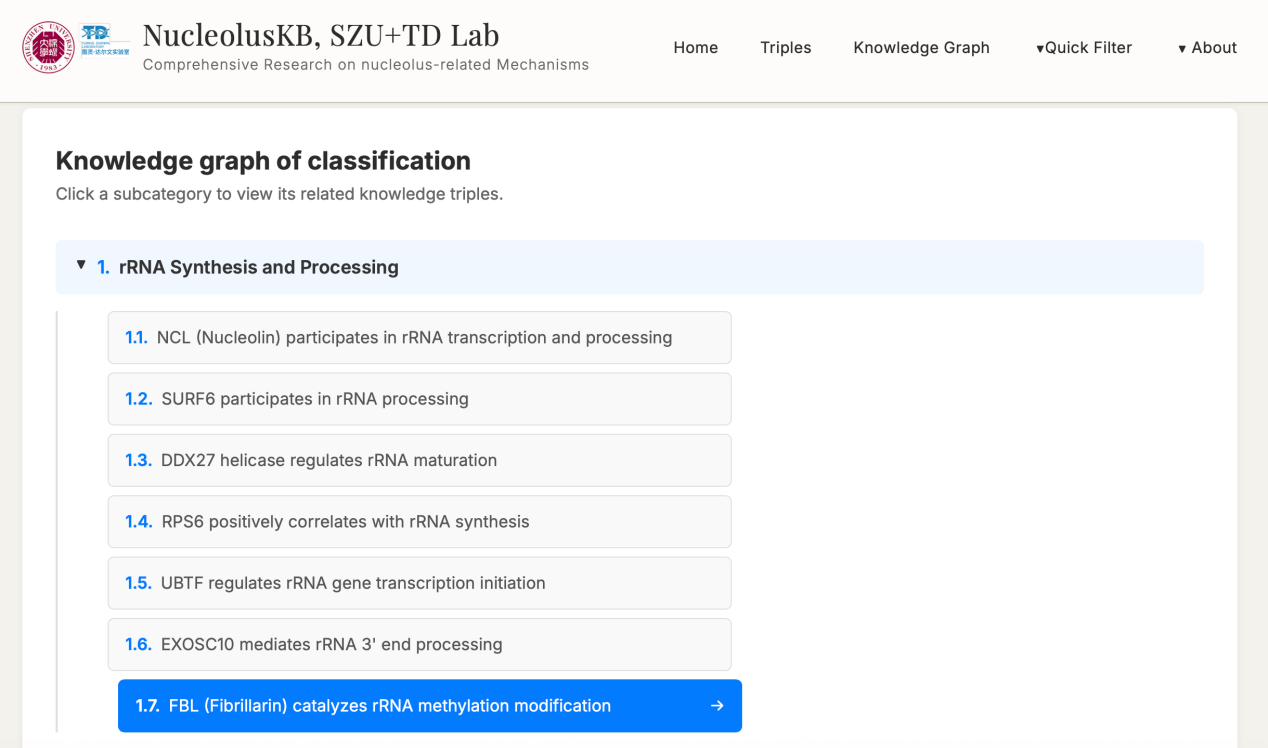
4.2 Knowledge Graph
Steps:
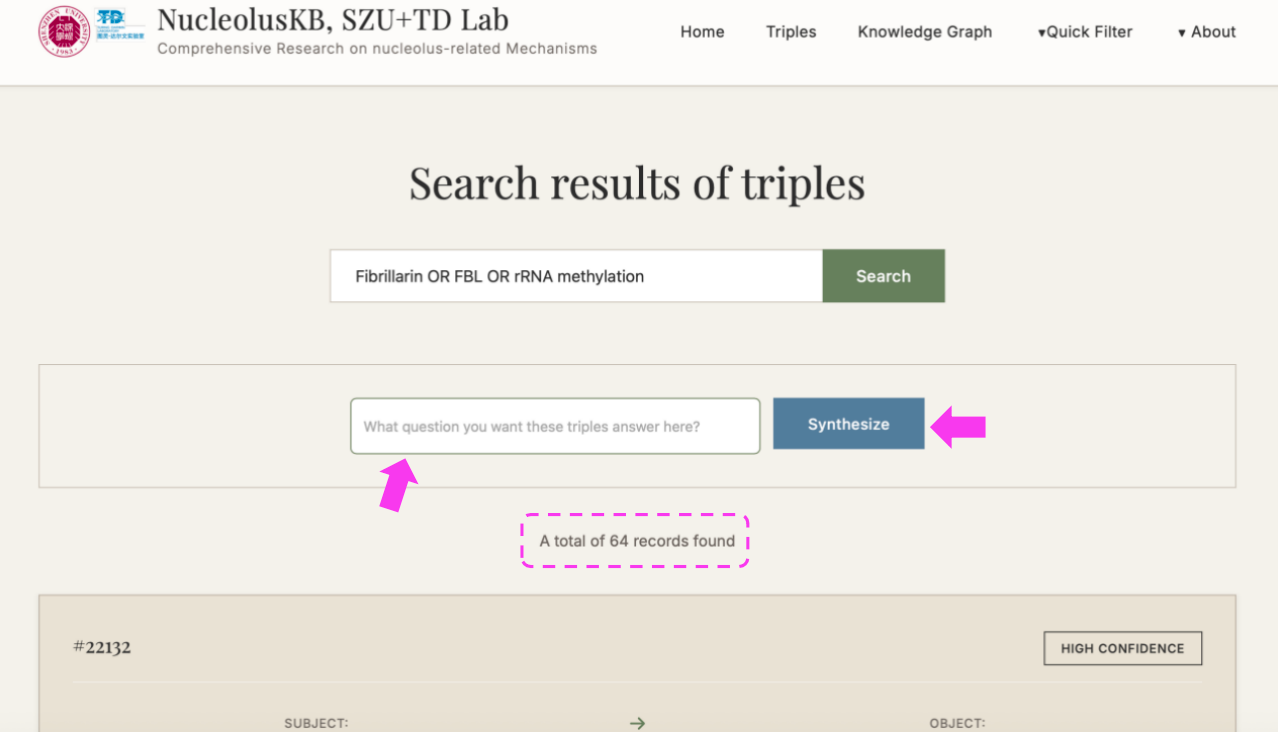
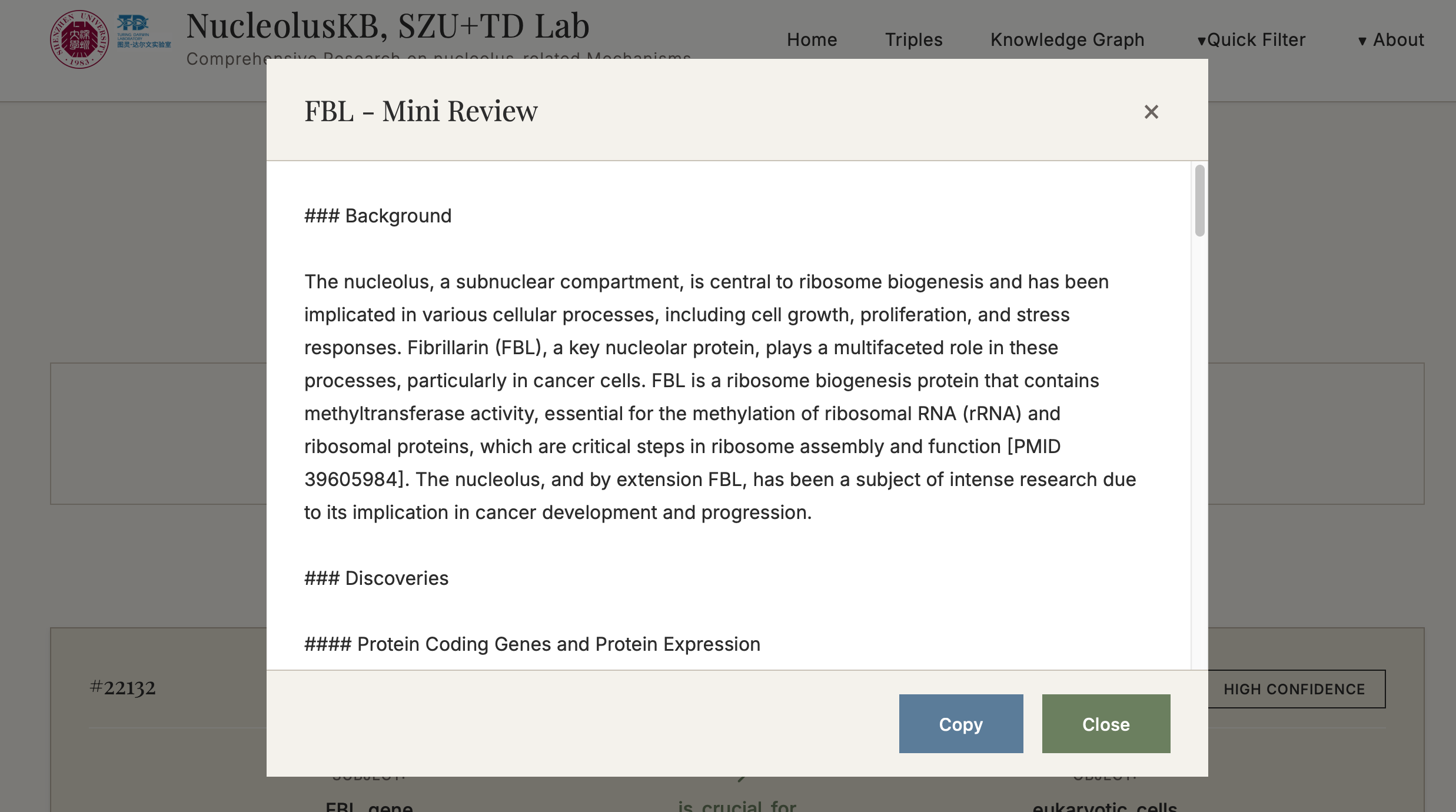
4.3 Generate Search Query
Steps:
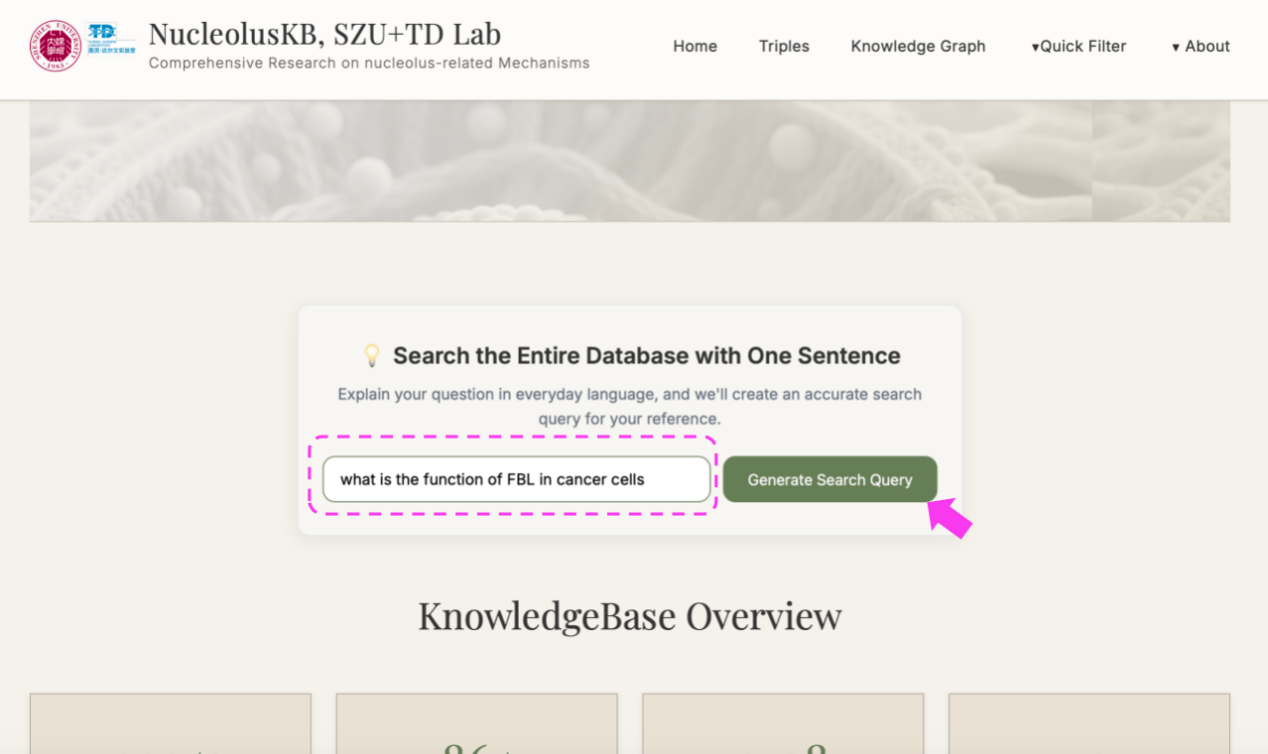
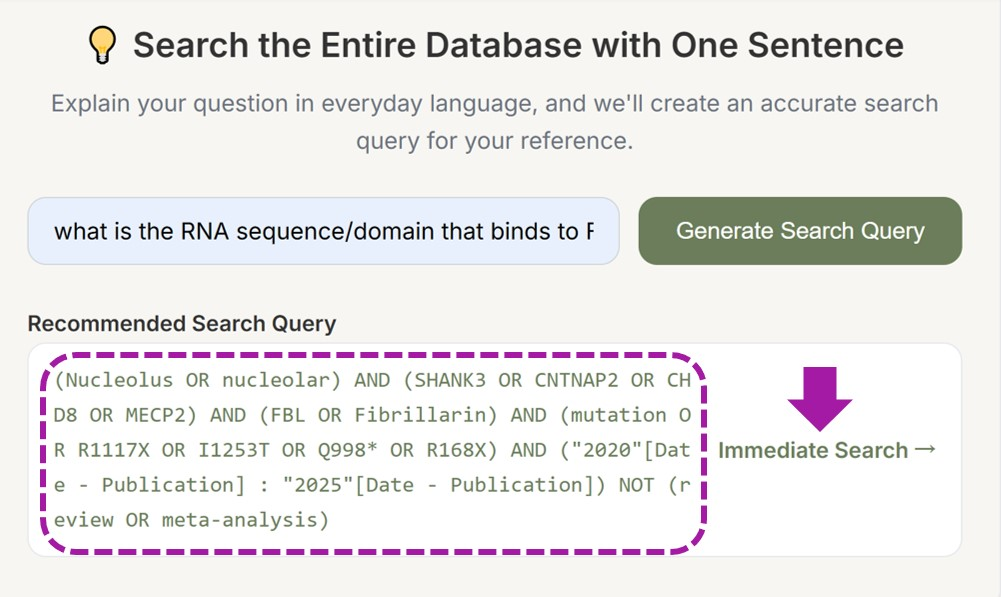
5. Advanced Features
5.1 AI Review Generation System
Function: Automatically generate 200-500 word academic reviews based on retrieved knowledge entries
Features:
- ✅ Automatic PMID citations included
- ✅ One-click copy functionality
- ✅ Based on evidence-based knowledge
- ✅ Academic writing standards
Usage Recommendations:
- Questions should be specific and clear
- Avoid overly broad inquiries
- Can iterate multiple times to optimize question description
5.2 Confidence Scoring System
| Evaluation Dimension | High Confidence | Medium Confidence | Low Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multicenter clinical trials | ✔ | ||
| Systematic reviews/Meta-analyses | ✔ | ||
| Large-sample clinical studies (n≥100) | ✔ | ||
| Standardized animal experiments (n≥30) | ✔ | ||
| Statistical P-value < 0.001 (highly significant difference) | ✔ | ||
| Verified by ≥5 independent studies | ✔ | ||
| Molecular mechanisms fully elucidated | ✔ | ||
| Direct clinical application value | ✔ | ||
| In vitro cell experiments | ✔ | ||
| Retrospective clinical studies | ✔ | ||
| Multi-dataset bioinformatics analysis | ✔ | ||
| Statistical P-value < 0.05 (significant difference) | ✔ | ||
| Verified by 2-4 studies | ✔ | ||
| Mechanisms basically clarified | ✔ | ||
| Potential clinical value | ✔ | ||
| Single cell line experiments | ✔ | ||
| Case reports | ✔ | ||
| Theoretical speculation or hypothesis | ✔ | ||
| Statistical P-value ≥ 0.05 (no significant difference) | ✔ | ||
| Single study report | ✔ | ||
| Mechanisms unclear | ✔ | ||
| Clinical significance unknown | ✔ |
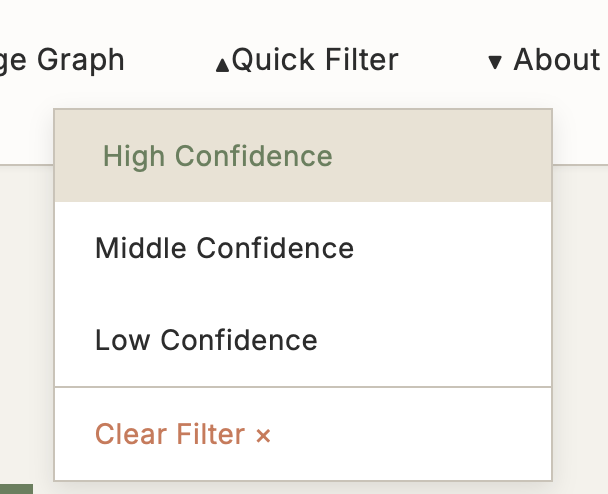
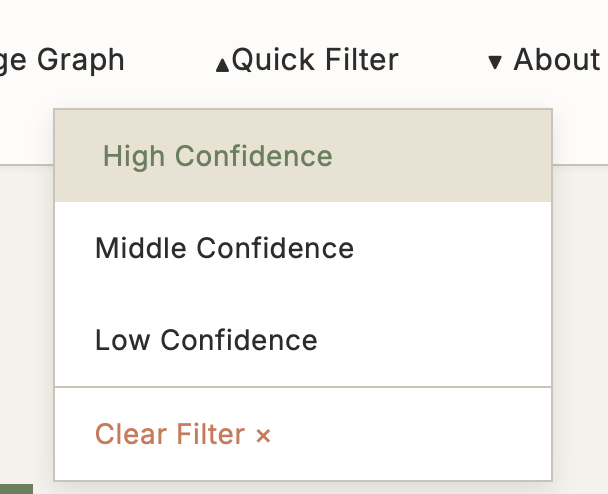
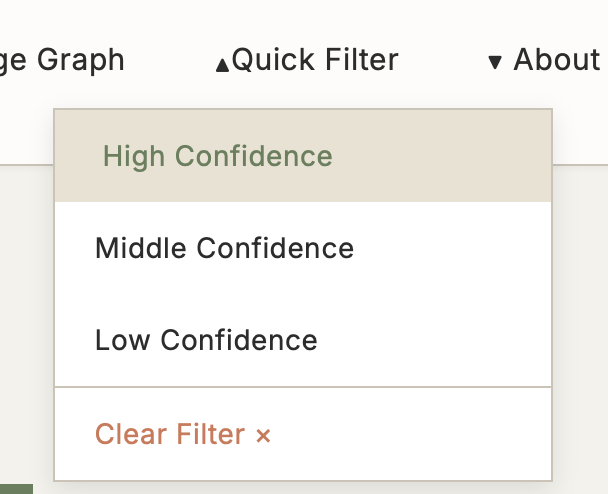
5.3 Quick Filter
Function: Preset confidence filters supporting multi-criteria rapid filtering
Use Cases:
- Large volume of results need quick filtering
- Focus only on high-quality evidence
- Filter results by specific criteria
6. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What to do when search returns no results?
A:
- Check keyword spelling
- Try synonyms or simplified terms
- On the homepage, use "Generate Search Query" for recommended keywords
- Try broader search terms
Q2: How to improve search accuracy?
A:
- Use standard gene/protein names
- Combine with confidence filtering
- Check "Details" for complete information
- Cross-validate multiple sources
Q3: How is AI review quality ensured?
A:
- Based on high-quality literature databases
- Includes original PMIDs for verification
- Confidence scoring assists judgment
- Recommend combining with professional knowledge
Q4: What is the data update frequency?
A:
- Regular updates from PubMed and other databases
- Check "About" page for specific update cycles
Q5: Can data be exported?
A:
- Reviews support one-click copying
- Contact administrator for detailed data export
Q6: What to do with technical issues?
A:
- Refresh page and retry
- Check network connection
- Review other FAQ answers
- Contact technical support: niyx@szu.edu.cn
7. Technical Specifications
7.1 Data Sources
- Primary Source: PubMed literature database
- Data Types: SPO triples, gene information, protein functions, disease associations, pathway, etc.
- Update Mechanism: Regular automatic updates
7.2 System Architecture
- Knowledge Extraction: Based on natural language processing technology
- Confidence Calculation: Multi-dimensional evidence strength assessment
- Search Engine: Supports keyword and semantic search
- AI Generation: Based on retrieval-augmented text generation
7.3 Usage Limitations
- Academic research use only
- Not for commercial purposes
- Proper source citation required
8. Contact Us
Technical Support
📧 Email: niyx@szu.edu.cn
🏢 Institution: Shenzhen University
Feedback and Suggestions
We welcome your feedback and suggestions! Please contact us via:
- Send user experience and improvement suggestions
- Report system bugs or technical issues
- Request new features or data updates
- Collaboration and exchange opportunities
Citation Information
If NKB helps your research, please cite appropriately in publications. Check the "About" page for specific citation information and format.
Appendix: Glossary
| Term | Full Name | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| SPO | Subject-Predicate-Object | Structured knowledge representation |
| PMID | PubMed Identifier | Unique identifier for PubMed articles |
| NPM1 | Nucleophosmin 1 | Nuclear phosphoprotein 1 |
| FBL | Fibrillarin | Nucleolar protein involved in rRNA processing |
| NKB | Nucleolus Knowledge Base | Specialized database for nucleolar biology |
💡 Usage Tip: Bookmark this page for easy reference. Happy researching!